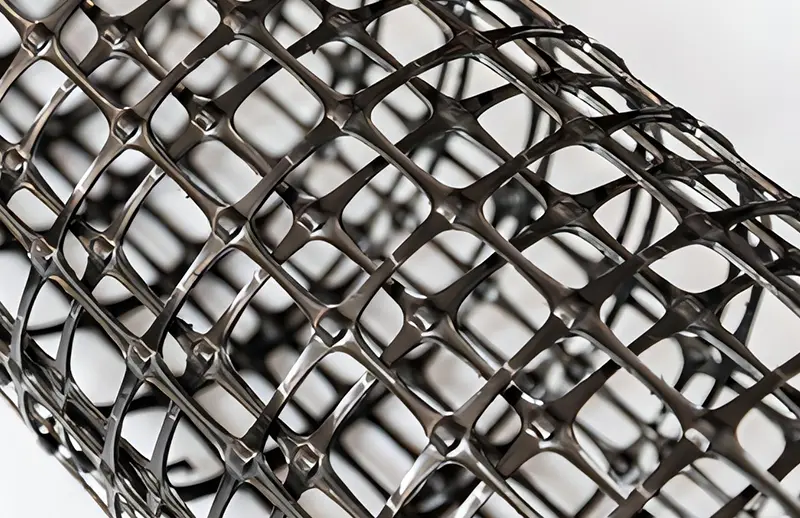
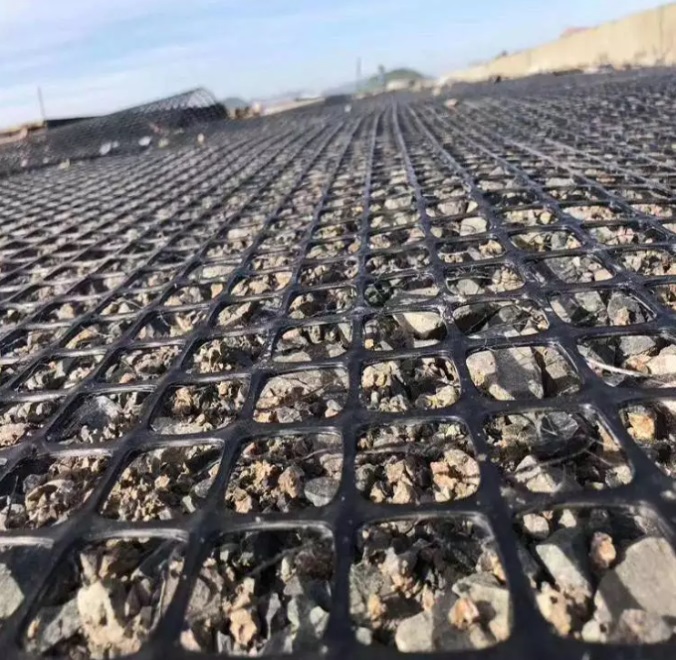
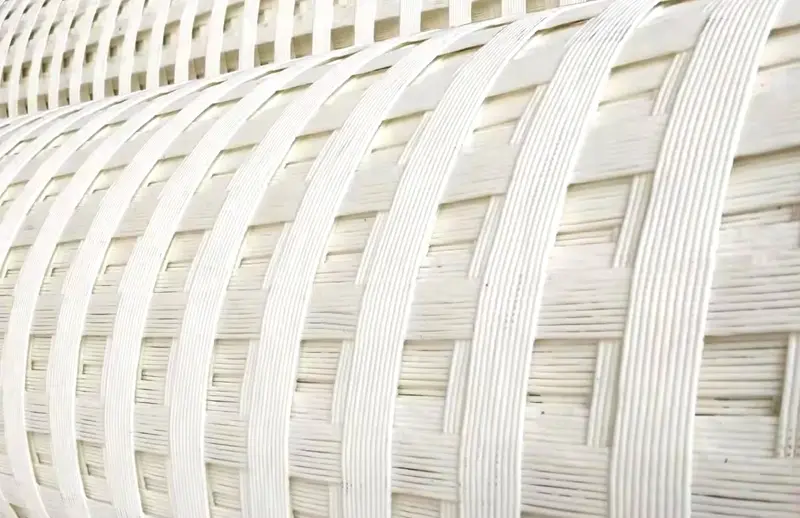
Plastic PP Geogrid
Weight:100g/m2-1200g/m2
Width:1-5.2m
Length:50-100m/roll
Material:100% Virgin PP
Type: biaxial and uniaxial
Plastic PP Geogrid is a geosynthetic material used primarily in civil engineering applications to reinforce soils. PP Geogrid is made of polypropylene material through extrusion, forming and punching before longitudinal and lateral stretching. PP geogrid is characterized by their high tensile strength and open apertures, which allow for effective interlocking with surrounding soil or aggregate. This material has considerable tensile strength in longitudinal and lateral directions. This chain structure can effectively bear and diffuse forces on soil and is applicable to large area permanent load bearing foundation as a reinforcement material.

This type of structure is usually exhibited by triaxial geogrid. They constitute rib-like bars that are organized in three directions and that are perpendicular to each other. This orientation is significant since it provides support and reinforcement from three different dimensions thus enhancing stability and strength.

This structure entails a single orientation of the rib-like bars. As opposed to the triangular structure, this type of structure has a relatively lower strength, especially in the transverse direction but has high tensile strength. Furthermore, the single orientation principle in this structure makes uniaxial geogrid suitable for applications that require reinforcement in a single direction such as slopes, wall retaining, and embankments.
Classification Criteria of Geogrid
Plastic geogrid can be classified into three main classifications according to the type of structure they possess. These include; uniaxial, biaxial and triaxial geogrid.
Uniaxial Plastic Geogrid
They possess ribs that are characteristically oriented in a one-way principal direction. They also have a high tensile strength spread along the direction of the ribs. As a consequence of this, they are commonly applied in the field of engineering in areas such as making pavement reinforcements, retaining walls, embankments, and steep slopes.
Biaxial Geogrid
Biaxial geogrid as opposed to uniaxial geogrid have a two-way rib orientation in both transverse and longitudinal directions. Due to this, the strength exerted from the two directions provides soil reinforcement in double perpendicular directions. Biaxial geogrid is commonly applied in the construction sector such as in pavement, load support, and road construction.
Triaxial Geogrid
They exhibit a triangular structure in that the ribs are characteristically oriented in three different directions that are perpendicular to each other. As opposed to biaxial geogrid, this type of geogrid provides strength and reinforcement from three different points that are perpendicular to each other. Similarly, they are also characterized by their high tensile strength and high load-bearing ability. They can be applied in areas such as wall retaining, stabilization of slopes as well as in load support systems.
Advantages of Plastic Geogrid
Plastic geogrid are termed advantageous in many ways as opposed to other types of geogrid. Some of these advantages are discussed below;
Durability
This can be attributed to their ability to resist corrosive chemicals which may lead to biological degradation. In the same way, Plastic geogrid is also resistant to moisture as well as UV rays since they maintain their structural status during such harsh environmental conditions.
Cost-Effective
As opposed to other types of geogrid, plastic geogrid are a relatively cheaper option. This is due to low costs of production as well as distribution. Likewise, they are easy to work with thus making them to be easily installed as compared to other types of geogrid.
High Tensile Strength
They can withstand high pressure and loads since the pressure is evenly distributed throughout the material. Consequently, they are suitable for stabilizing soils specifically improving the bearing capacity of soils.
Resistant to Corrosion
Compared to other types of geogrid, this type of geogrid is usually resistant to rust and corrosion. For example, geogrid made of metal and other related materials are highly likely to be affected by rust since they react in the presence of oxygen and moisture to form rust.
| Index Properties | Test Method | DK15 | DK20 | DK30 | DK40 | DK50 | |
| Ultimate Tensile Strength KN/m) | MD | ASTM D 6637 | 15 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 |
| CD | |||||||
| Elongation at Maximum Load (%) | MD | 13 | |||||
| CD | |||||||
| Tensile Strength at 2% Elongation (KN/m) | MD | 5 | 7.5 | 10.5 | 14 | 18 | |
| CD | |||||||
| Tensile Strength at 5% Elongation (KN/m) | MD | 7 | 14 | 21 | 28 | 35 | |
| CD | |||||||
| Minimum Carbon Black(%) | ASTM D 4218 | 2 | |||||
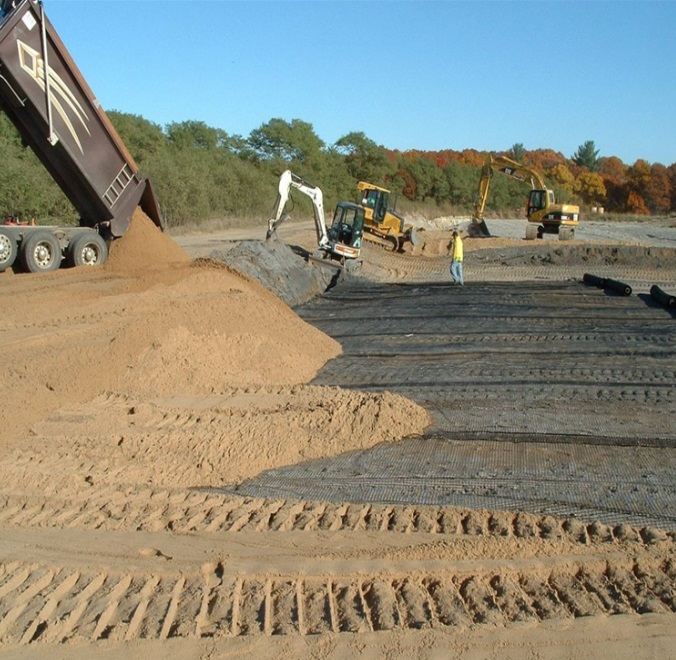

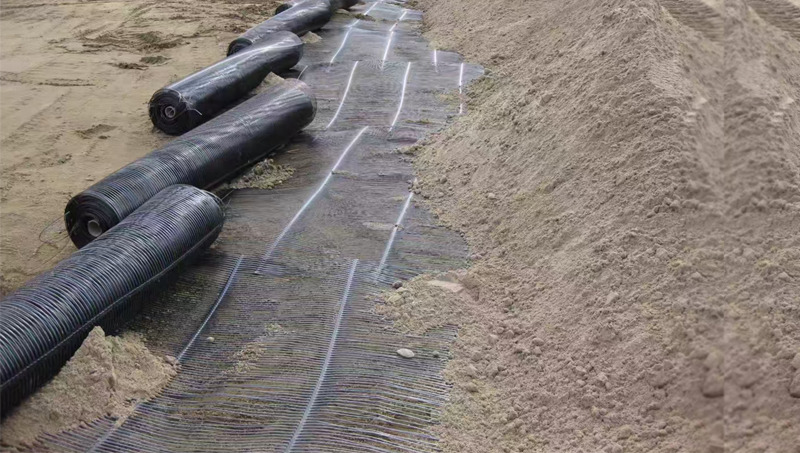
Highway and Railway Engineering: PP geogrid is used for subgrade reinforcement to evenly distribute the load and reduce subgrade settlement. PP geogrid is especially suitable for soft soil foundation sections, enhancing the stability of the roadbed and prolonging the service life of the highway or railway.
Slope Protection Projects: When laid on slopes, PP geogrid can prevent soil erosion and landslides by increasing the shear strength of the soil and improving the stability of the slope.
Dams and Embankments: In water conservancy projects, PP geogrid is used to reinforce dams and embankments, enhancing their stability and preventing seepage and deformation.
Landfill Sites: PP geogrid is used in the foundation and sidewalls of landfills to prevent settlement and displacement of the landfill, and to isolate and protect the surrounding soil and groundwater.
Mining Engineering: In underground coal mines, PP geogrid can be used as a false roof net, which is fire-resistant and antistatic, providing safety protection for mining operations.
Geogrid materials
Various types of materials can be suitable for the making of geosynthetic compounds. The type of material used therefore determines the features and uses of a particular type of geogrid. Below are some of the best materials used to make geogrid.
Steel Plastic Geogrid
These types of geogrid are made from steel wires that have a high tensile strength in conjunction with other additives such as treatment chemicals and polyethylene through processes such as extrusion. The belt achieved through this process is thereafter woven at specific distances both horizontally and vertically and joints are joined together by welding.
Polyester Geogrid
They are also referred to as warp-knitted geogrid. They offer strength to buildings and roads since they strongly compact gravel and soil. This is due to their high tear and tensile strength thus making them to be suitable where the soil is very loose.
PP Mining Geogrid
They are composed of polymers and polypropylene compounds achieved through processes such as stretching and extrusion. Are mainly suitable for underground projects such as coal mining. They are characterized by their resistant nature to corrosion, high tensile strength as well as ease of installation.
Fiberglass Geogrid
They are made by coating and weaving glass fiber that has high tensile modulus, high lateral and longitudinal tensile strength as well as low elongation. They are commonly applied in a variety of fields such as in making pavements, roads, and walls that require strong reinforcement.
Features of Plastic PP Geogrid
1.High Strength:Plastic PP Geogrid has high tensile strength, providing good reinforcement for soil and enhancing the bearing capacity of the foundation.
2.Good Stability: With a stable structure,Plastic PP Geogrid can maintain its shape and performance well under various loads and environmental conditions.
3.Anti-aging and Corrosion Resistance:Plastic PP Geogrid has good resistance to chemicals, UV rays and other environmental factors. It is not easy to age and corrode, thus having a long service life.
4.Lightweight and Easy to Construct: Plastic PP Geogrid is lighter in weight compared to traditional materials, which makes it convenient to transport and install. It can be easily laid and adjusted according to the construction requirements.
5.Good Compatibility with Soil:Plastic PP Geogrid can interact effectively with the soil, interlocking with the soil particles, which improves the overall stability of the soil mass.