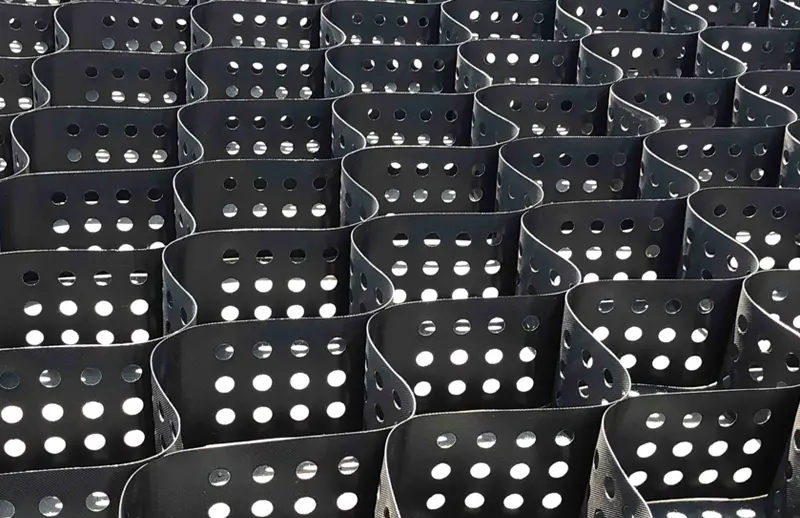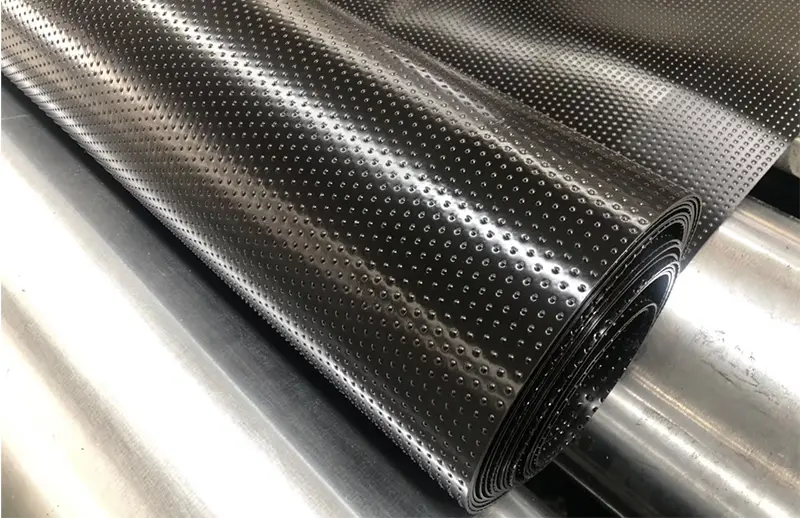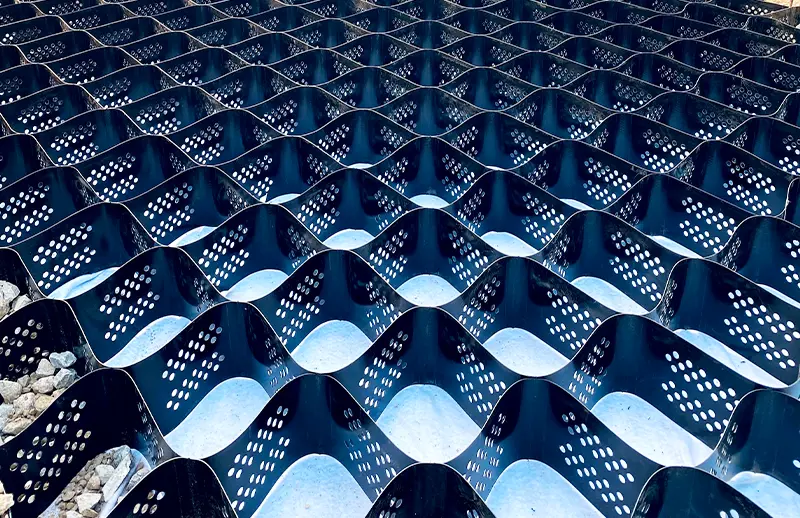
HDPE Smooth Surface Geocell
Product Name HDPE Geocell
Cell Depth 50, 75, 100, 125, 150, 200mm
Weld Spacing 330, 356, 400, 445, 660, 712mm
Thickness(Textured) 1.5, 1.52, 1.6mm
Thickness(Smooth) 1.1, 1.2mm
Colour Black, Sandy, Green
Standard ASTM, ISO

The wall of each cell within a perforated geocell system features a series of uniformly spaced, minute openings that help disperse stress and minimize disfigurement. The material’s structural integrity relies heavily on the rigidity of the weld and the strip.
The punctured and textured surface raises the angle of friction between the cell wall and aggregate infill. This promotes better aggregate confinement and higher general load distribution. Moreover, the perforations allow for lateral chamber-to-chamber drainage of excess surface and ground water, minimizing the adverse impacts of trafficking above saturated soils.

Also referred to as solid wall geocells, non-perforated geocell confinement systems lack any openings across the cells wall. They are suitable for applications in which drainage of water is not a major consideration.
You can also employ them where there is need for infill materials containment inside the cells. The functions of non-perforated geocells are for reinforcement, load support, and stabilization of soil.

Often, geocell grids come in collapsed state that is easy to expand. You can expand them fast and effortlessly, and place the infill manually, using simple construction equipment or tools.
Rectangular stretcher frames usually simplify the geocell installation process by expanding the dimensioned parts accordingly. The multipurpose stretcher frames help in ensuring correct sectional geometry, and are employed only during infilling.
Individual geocell parts can be coupled together through, stapling, anchoring, or using clip arms. For increasingly sophisticated constructions, extra fittings like tendons and anchoring devices might be necessary.
- Product Name HDPE Geocell
- Cell Depth 50, 75, 100, 125, 150, 200mm
- Weld Spacing 330, 356, 400, 445, 660, 712mm
- Thickness(Textured) 1.5, 1.52, 1.6mm
- Thickness(Smooth) 1.1, 1.2mm
- Colour Black, Sandy, Green
- Standard ASTM, ISO
| Index Properties | Test Method | Units | Values | ||||||||||||
| Material | 100% Virgin HDPE | ||||||||||||||
| Carbon Black Content | ASTM D 1603 | % | ≥1.5 | ||||||||||||
| Density | ASTM D 1505 | g/cm3 | 0.935-0.965 | ||||||||||||
| Sheet Thickness +5% | ASTM D 5199 | mm | 1.5 | ||||||||||||
| Seam Peel Strength | USACE GL-86-19 | KN/m | ≥14.2 | ||||||||||||
| Tensile Strength at Yield | ASTM D 638 | KN/m | ≥22 | ||||||||||||
| Environmental Stress Crack Resistance ESCR | ASTM D 1693 | hrs | ≥5000 | ||||||||||||
| Oxidation Induction Time OlT | ASTM D 3895 | min | ≥150 | ||||||||||||
| Type No. | DK330 | DK356 | DK445 | DK660 | DK712 | ||||||||||
| Welding Distance(mm)3% | 330 | 356 | 445 | 660 | 712 | ||||||||||
| Cell Depth(mm)+3% | 50,75, 100,150,200,250 | ||||||||||||||
| Dimensions | |||||||||||||||
| Expanded Cell Size (widthxlength)(mm)+3% | 250×210 | 260 x225 | 320 x 288 | 470×450 | 510×475 | ||||||||||
| Expanded Cell Numbers (widthxlength) | 10×34 | 9 x 34 | 8 x 34 | 5 x34 | 5 x 34 | ||||||||||
| Expanded Section Size (widthxlength)(m)+3% | 2.50 x7.14 | 2.34 x 7.65 | 2.56 x 9.8 | 2.35 x 15.3 | 2.55 x 16.15 | ||||||||||
| Expanded Section Area (m2)+5% | 17.85 | 17.9 | 25.1 | 36 | 41.2 | ||||||||||
Road Building
Geocells grids serve to better all-around road performance, limit pavement breakdown, as well as boost load-bearing potential.
Stabilization of Slopes
The geosynthetic systems are effective in soil erosion prevention, minimizing landslides, and giving support, thus boosting slope stability.
Retaining Walls
Geocell systems can be utilized in the construction of retaining walls as they offer reinforcement to the walls and are very flexible. This flexibility allows the geocell to be installed around pipes, irregular structures and curves.
Landscaping and Erosion Mitigation
Using Geocell products to construct green spaces, gardens, and terraces, they help in enhancing the topography aesthetic.
Mining
Geocell materials are applied in mining operations to improve stability, control erosion, and enhance environmental containment. This protects the mine from potential collapse.
Channel Protection
Geocells are commonly used to stabilize and reinforce the banks of channels, rivers, and other water bodies. They offer effective erosion control and enhance the overall stability of the channel hence maintaining the integrity of the watercourse.
Materials Used in Geocell

Geocells manufacturers normally use a number of materials for production of the confinement systems. The material type utilized in geocells manufacturing considerably affect the performance, cost and durability of the product. Every geocell material possesses its individual pros and cons, and the selection relies on parameters like site conditions, project specifications, environmental aspects, and budget.
The common materials used in geocell production comprise of:
High-Density Polyethylene – HDPE is popular for its high chemical resistance, strength, and longevity. HDPE geocells are the most preferred because of their outstanding properties, consisting of resistance to moisture, chemical and ultraviolet radiation degeneration.
They are easy to mold into required honeycomb structure due to their flexibility. HDPE geocells grids offer superior confinement, stabilization, and load distribution abilities.
Polypropylene (PP) – Polypropylene is another thermoplastic polymer material for geocell manufacturing with properties same as those of HDPE. They commonly find application in projects where cost considerations or chemical compatibility are of great concern.
Polyester (PET) – Though polyester is not a common geocell material, it is still employed in some applications. Polyester geocell manufacturing often uses high-tenacity polyester fiber that is coated further using other polymer material.
Polyester geocells systems provide superior tensile strength and outstanding chemical and biological deterioration resistance. They are perfect for geocell applications needing greater rigidity and strength in comparison to HDPE geocells.
Recycled Materials – Some geocell manufacturers use recycled plastics in the production process to minimize environmental effects and encourage sustainability. They can utilize recycled PP or HDPE to produce geocells whilst retaining their fundamental properties. This helps in waste minimization and promote the circular economy concept.
How Geocells Work
The main purpose of geocell ground grids is to ensure that soil is protected and stabilized. They increase the efficacy of standard civil building and erosion prevention materials.
The materials are 3D, expandable panels fabricated using polymeric materials. When you expand them during geocell installation, the intertwined strips develop the walls of elastic, 3D cellular structures. It is in these structures that you place and compact the stipulated infill materials.
Consequently, the expansion forms a free-draining system, which locks up the infill substances in place. It also inhibits mass displacement by offering confinement via tensile reinforcement. The operational and structural properties of infills and topsoil are strengthened by the geocell confinement system.
The selection of infill material is basically dictated by the intensity and nature of expected working strains. You should also consider the cost and availability of candidate materials, and the aesthetic necessity for a completely vegetated look. prevalent geocell filler products include concrete, aggregates, and cultivated surface soil.