There is wide use of geogrid materials in the building of earth-retaining and earth-supported structures, including mechanically-stabilized earth steep slopes, and retaining walls. Some of the ordinary uses of geogrids are:
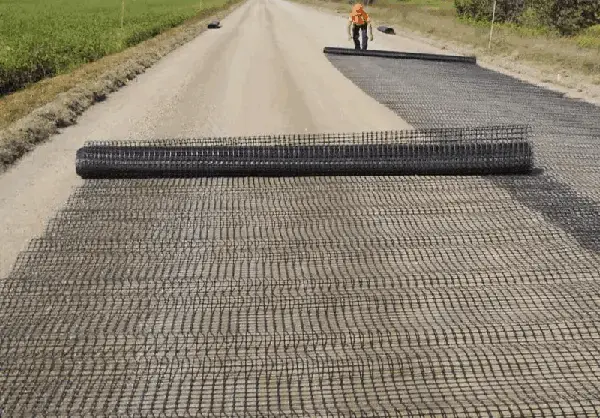
. Geogrids in Roads, Railways and Pavement
Geogrids are vital in improving subgrade, reinforcing the surface courses, sub-base and bad course in trafficked areas. Reinforcing railway ballast using geogrids inhibits their outward displacement and minimizes settlement. With soft subgrade, rigid geogrids are more efficient in comparison to flexible types since the latter reacts faster to the exerted load.
. Geogrids Material in Retaining Wall
Geogrids are valuable in backfill stabilization within retaining walls. The friction angle determines how stable the earth retaining wall will be.
The Geogrid product performance within the wall is dependent on the stress and creep relaxation features. You must install high-strength geogrid material at the retaining wall center or decrease the spacing of the geogrid reinforcement.
. Geogrids Materials in Soil Foundation
Foundation works often employ both biaxial and uniaxial geogrid types. The intermeshing capability of the aggregates and geogrid helps in attaining great stability. You can integrate geocell reinforcement to manage the vibrations.
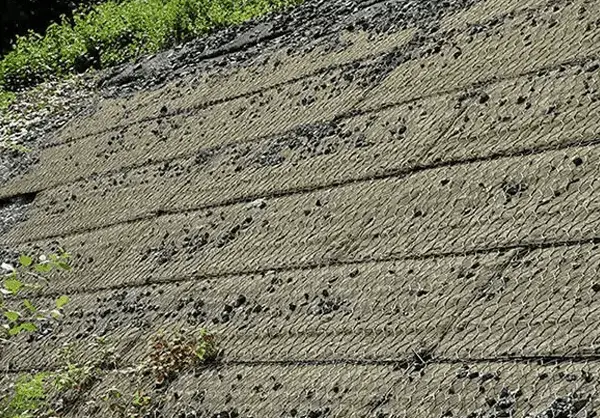
.Geogrids Materials in Steep Slope Stabilization
Applying geogrids to reinforce steep slopes affects majorly the stability and distortion of the slope. The geogrid material length largely determines the bearing capability. For best performance, use geogrid pore size that is about 0.2 times the footing width. This lowers earth embankment displacement and raises safety, which is due to extended length and greater tensile strength.